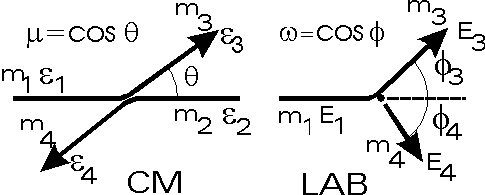
|
|
|
Two-body reactions, such as elastic scattering, neutron inelastic
scattering to a level, or (p,n) to a discrete level, obey simple
kinematical formulas that couple the outgoing energy E' ,
the incident energy E, and the scattering cosine μ.
The parameters for two-body collisions are shown below in both
center-of-mass and laboratory reference frames:
|
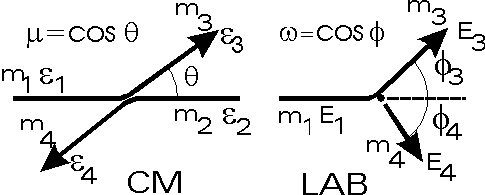
|
The non-relativistic kinematical formulas can now be written as
follows:
|
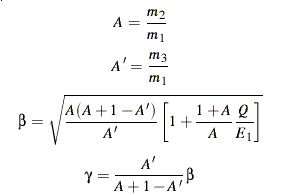
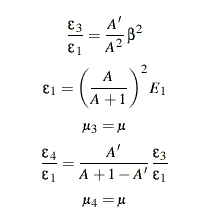
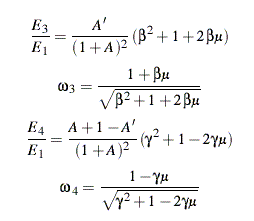
|
If the incident and scattered particles are the same, A'=1,
and these formulas reduce to the more familiar set often given
for neutron scattering. The elastic reaction corresponds to
A'=1 and Q=0. Note that the energy-angle distribution of the emitted particle and the full energy-angle distribution of the recoil nucleus are completely determined by A, A', Q, and the angular distribution f(E,μ). |
| NEXT | INDEX |
| 15 December 2012 | T-2 Nuclear Information Service | ryxm@lanl.gov |